Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have a negative effect on health.[1] People are generally considered obese when their body mass index (BMI), a measurement obtained by dividing a person's weight by the square of the person's height, is over 30 kg/m2, with the range 25–30 kg/m2defined as overweight.[1] Some East Asiancountries use lower values.[8] Obesity increases the likelihood of various diseases and conditions, particularly cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, osteoarthritisand depression.[2][3]
Obesity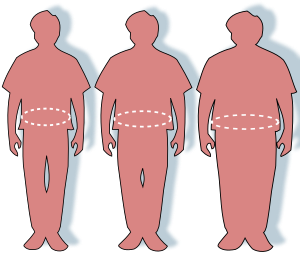 Silhouettes and waist circumferencesrepresenting optimal, overweight, and obeseSpecialtyEndocrinologySymptomsIncreased fat[1]ComplicationsCardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, osteoarthritis, depression[2][3]CausesExcessive food, lack of exercise, genetics[1][4]Diagnostic methodBMI > 30 kg/m2[1]PreventionSocietal changes, personal choices[1]TreatmentDiet, exercise, medications, surgery[1][5][6]PrognosisReduce life expectancy[2]Frequency700 million / 12% (2015)[7]
Silhouettes and waist circumferencesrepresenting optimal, overweight, and obeseSpecialtyEndocrinologySymptomsIncreased fat[1]ComplicationsCardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, certain types of cancer, osteoarthritis, depression[2][3]CausesExcessive food, lack of exercise, genetics[1][4]Diagnostic methodBMI > 30 kg/m2[1]PreventionSocietal changes, personal choices[1]TreatmentDiet, exercise, medications, surgery[1][5][6]PrognosisReduce life expectancy[2]Frequency700 million / 12% (2015)[7]
Obesity is most commonly caused by a combination of excessive food intake, lack of physical activity, and genetic susceptibility.[1][4] A few cases are caused primarily by genes, endocrine disorders, medications, or mental disorder.[9] The view that obese people eat little yet gain weight due to a slow metabolism is not generally supported.[10] On average, obese people have a greater energy expenditure than their normal counterparts due to the energy required to maintain an increased body mass.[10][11]
Obesity is mostly preventable through a combination of social changes and personal choices.[1] Changes to diet and exercising are the main treatments.[2] Diet quality can be improved by reducing the consumption of energy-dense foods, such as those high in fat and sugars, and by increasing the intake of dietary fiber.[1] Medications may be used, along with a suitable diet, to reduce appetite or decrease fat absorption.[5] If diet, exercise, and medication are not effective, a gastric balloon or surgery may be performed to reduce stomach volume or length of the intestines, leading to feeling full earlier or a reduced ability to absorb nutrients from food.[6][12]
Obesity is a leading preventable cause of death worldwide, with increasing rates in adults and children.[1][13] In 2015, 600 million adults (12%) and 100 million children were obese.[7] Obesity is more common in women than men.[1] Authorities view it as one of the most serious public health problems of the 21st century.[14] Obesity is stigmatized in much of the modern world (particularly in the Western world), though it was seen as a symbol of wealth and fertility at other times in history and still is in some parts of the world.[2][15] In 2013, the American Medical Association classified obesity as a disease

No comments:
Post a Comment
Thankyou